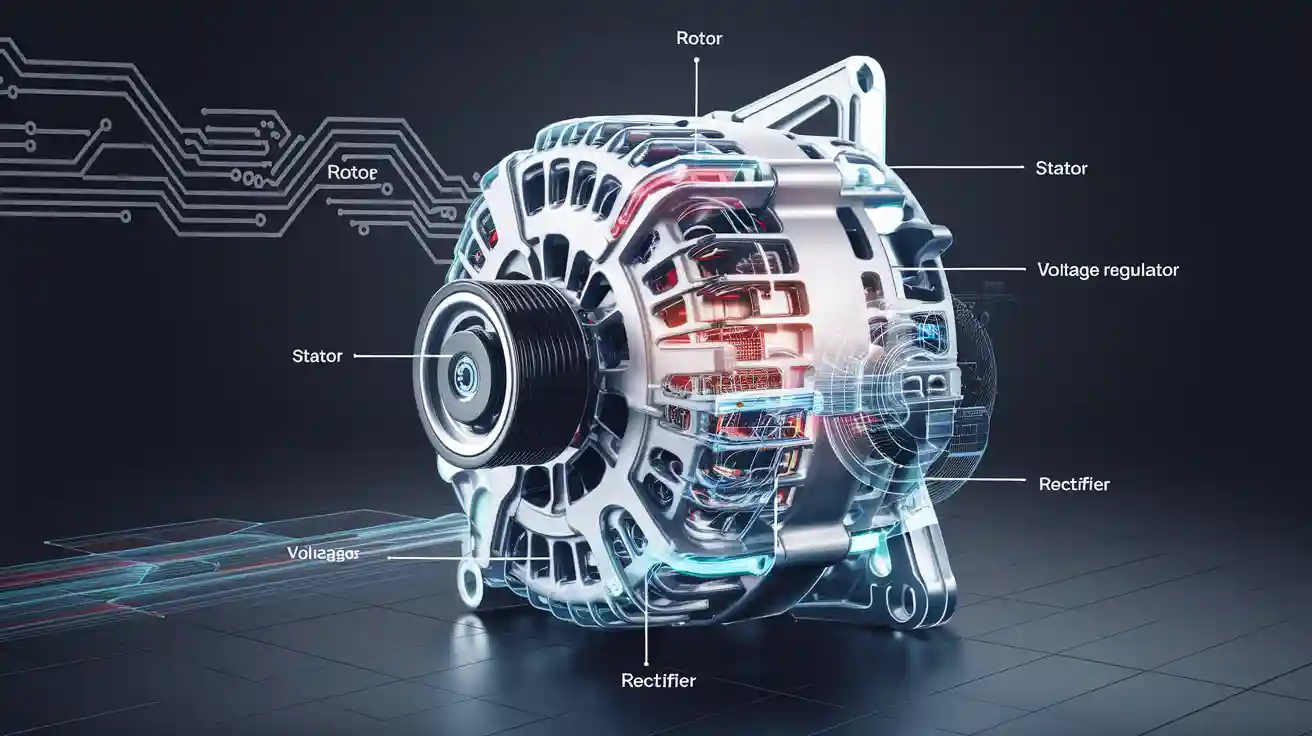
When you observe the Parts Of The Alternator, there are several vital components. These parts work together to produce power for your vehicle. Each part has a special job. They help your car receive the electricity it requires.
The rotor also rotates in the alternator. It makes a magnetic field.
The stator does not move. It's got coils for making voltage.
The power is altered by the rectifier and voltage regulator. They enable your car to use it.
These components assist each other in maintaining your car's performance.
Components of an alternator
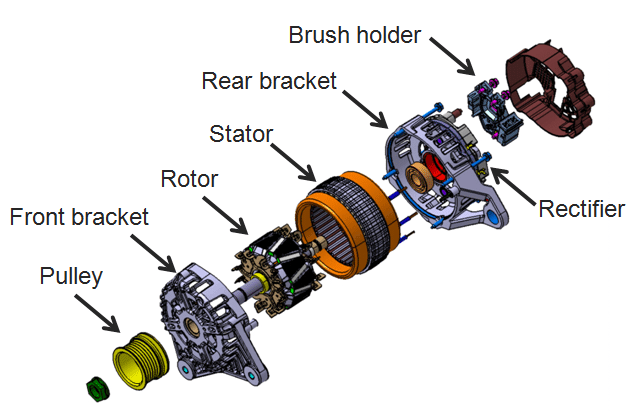
If you learn about the alternator parts, you will know how your car makes electricity. Each part has its own job. These jobs help turn engine power into electrical energy. Let's look at the most important parts and what they do:
Quick Reference Table:
Here's a table to help you see the main component parts and their basic functions:
Part Name | Basic Function |
|---|---|
Rotor | Rotates inside the stator to create a magnetic field and generate AC. |
Stator | Holds windings; produces voltage when the rotor spins inside. |
Pulley | Transfers engine power to the alternator; helps maintain stable operation. |
Slip Rings | Provide electrical contact between the spinning rotor and stationary parts. |
Brushes | Maintain contact with slip rings to transfer current. |
Voltage Regulator | Controls the alternator's output voltage. |
Diode Rectifier | Converts AC to DC for the car's electrical system. |
Bearings | Support the rotor shaft and allow smooth rotation. |
Cooling Fan | Draws air to cool the alternator and prevent overheating. |
Housing | Protects internal parts and helps with heat dissipation. |
Alternator Rotor
Source from Wiki:
In mechanical engineering, a rotor belongs to the rotating mechanical components of a machine, and is the moving part of a rotary actuator, electric motor, loudspeaker, or other rotating device. The engine to your car turns the rotor with a belt and puley, when your car is started. The rotor creates a powerful magnetic field as it rotates. Steel or iron are good choices for the material of most of the rotors. These materials contribute to a strong magnetic field and save energy. There are rotors that use copper to operate more efficiently and last longer. The rotor creates the magnetic field, for the stator.
Alternator Stator
The stator does not move. It goes around the rotor. It has wire coils called windings. When the rotor spins, its magnetic field moves past the windings. This makes electricity in the stator. Most stators have three sets of windings. These make three-phase AC power. Later, this power is changed to DC for your car. Stators can have different winding patterns. Star (WYE) gives more voltage at low speeds. Delta gives more current.
Pulley
The pulley is attached to the rotor shaft. It connects to the engine with a belt. When the engine runs, it turns the pulley. This makes the rotor spin. Many new alternators use a clutch pulley. This lets the alternator keep spinning if the engine slows down fast. It helps stop the belt from wearing out. Most cars use multi-groove pulleys. Some use overrunning pulleys to make less noise and vibration.

Slip Rings
Slip rings are metal rings on the rotor shaft. They let electricity flow from the brushes to the spinning rotor. Slip rings are usually made of copper or copper alloys. This helps them make good contact. Some slip rings have special coatings to last longer. The slip rings and brushes work together. They keep the rotor powered while it spins. This keeps the magnetic field strong.
Brushes
Brushes are small blocks made of carbon. They press against the slip rings. Brushes carry electricity from the battery to the rotor. Brushes wear down over time. This is because they always rub against the slip rings. Most brushes last between 60,000 and 100,000 miles. If brushes wear out, your lights may get dim. You might also see a battery warning light.
Voltage Regulator
The voltage regulator determines how much voltage is fed into your car's battery. It stabilizes the voltage, even as the engine speed fluctuates. The newer voltage regulators are electronic. These circuits control the magnetic field of the rotor. Some vehicles have the regulator built into the alternator. Others have it outside. The charger prevents your battery from being overcharged. It's also good for making your car's electronics work right.
Diode Rectifier
The diode rectifier changes AC power to DC power. Your car needs DC power to work. The rectifier uses diodes. Diodes only let electricity flow one way. This is called rectification. If a diode breaks, the alternator may not charge the battery. You might see flickering lights. The rectifier is important for giving your car the right kind of electricity.
Bearings
Bearings help the rotor spin smoothly. Most alternators use deep groove ball bearings. These can handle high speeds and heavy loads. Good bearings lower friction and noise. If a bearing wears out, you may hear a grinding sound. The alternator may not work right. Bearings usually last as long as the alternator. But rough driving or dirt can make them wear out faster.
Cooling Fan
Cold air is sucked through the alternator by the cooling fan. This prevents it form becoming too hot. When the alternator runs, it generates heat. The parts are cooled by a fan which blows cool air thereover. This keeps everything at a safe level. The alternator, without a fan, could get too hot, breaking down. Some alternators contain the fan in the interior. Others have it outside.
Housing
The housing is the outer case of an alternator. It keeps the internal components of the speaker free from dirt and from water. The majority of hulls have been constructed of aluminum. Aluminum is strong, light and does a good job of dissipating heat. The case keeps all the components together. It is also what allows the alternator to stay quiet. Some cases have fins to aid in cooling the alternator further.
Tip:
When you know the parts of an alternator, you’ll know if it is not working properly early. This serves to keep your car in good running condition.
Components of an alternator have a distinct function. Knowing the basics can help you maintain your car. You will also know what to look for if something goes wrong.
How alternators work
Electricity Generation
By these methods, you will have an idea of how the components of the Alternator operate:
The motor powers a drive belt that turns the pulley connected to the alternator.
The rotor is turned inside the alternator by the pulley.
This electrical current from brushes and slip rings is directed into the rotor's windings. This results in a powerful magnetic field.
The rotor magnet field sweeps past the stator's coils as it rotates.
The stator, which does not move, contains wire windings that intercept this moving magnetic field. This induces the stator with a induced current (AC).
That diode rectifier converts the AC to DC current which your car can use.
The voltage regulator monitors the output and maintains the voltage/drops the voltage as necessary to keep it constant, so your car's battery and electronics don't get hurt.
The cooling fan and housing help dissipate heat, so that the alternator will not overheat.
Tip:
If you follow these steps you should be able to see how each part plays a role in producing electricity for your car.
Powering The Vehicle
When your engine runs, the alternator supplies power to all the electrical systems in your car. It keeps the battery charged and provides steady electricity for things like headlights, the radio, and the ignition system. The alternator keeps the voltage around 14 volts, so every part gets the right amount of power. Unlike the battery, which stores energy, the alternator acts as the main source of electricity while you drive. This teamwork between the Parts Of The Alternator makes sure your car runs smoothly and all systems work as they should.
Now you know the Parts Of The Alternator. Each part helps your car make electricity. The rotor spins and makes a magnetic field. The stator uses this field to make power. The rectifier changes the power so your car can use it. The voltage regulator keeps things safe. If you know these parts, you can find problems early. This helps your car run well. You can also talk to mechanics more easily. You will take better care of your car.
FAQ
What if one Alternator goes down?
If one of them goes bad, your car could suddenly lose power or exhibit warning lights. You could see dim headlights or a dead battery. You really oughta test the alternator pretty soon before you find yourself stranded.
What are signs that you need to replace your alternator brushes?
You might also have a battery warning light that comes on, or you could see a flickering light issue. Occasionally, your car may struggle to start. Brushes that gets too worn can be the cause of this and similar problems. Take them to a mechanic to have them checked.
Can You Drive With A Bad Alternator Bearing?
You can continue to drive for a little while, but it will start grinding or squealing. Damaged bearings can do further harm. The problem should be repaired as soon as possible to avoid more extensive repairs.
Why does the alternator need a cooling fan?
The alternator makes heat when it works. The cooling fan moves air to keep the parts cool. This helps the alternator last longer and work better.
Are all alternators made with the same components?
The majority of alternators share the same components, like the rotor, stator and rectifier. Some might have added features like onboard voltage regulators or unique pulleys. Be sure to consult your car's manual for specifics.
How to Choose a right Alternator supplier that works for your business?
1. Fast Matching = Lower Time Cost
2. Reliable Lead Times = Less Risk
3. Flexible MOQ = Better Cash Flow
4. Customization Support = More Value for Your Brand
Knowing this will help you choose a supplier with more direction.



